QPixmap¶
Inherited by: QBitmap
Synopsis¶
Functions¶
- def alphaChannel ()
- def cacheKey ()
- def convertFromImage (img[, flags=Qt.AutoColor])
- def copy ([rect=QRect()])
- def copy (x, y, width, height)
- def createHeuristicMask ([clipTight=true])
- def createMaskFromColor (maskColor)
- def createMaskFromColor (maskColor, mode)
- def deref ()
- def doImageIO (io, quality)
- def fill ([fillColor=Qt.white])
- def fill (widget, ofs)
- def fill (widget, xofs, yofs)
- def hasAlpha ()
- def hasAlphaChannel ()
- def init (arg__1, arg__2, arg__3)
- def init (arg__1, arg__2[, arg__3=PixmapType])
- def isNull ()
- def isQBitmap ()
- def load (fileName[, format=0[, flags=Qt.AutoColor]])
- def loadFromData (buf[, format=0[, flags=Qt.AutoColor]])
- def loadFromData (data[, format=0[, flags=Qt.AutoColor]])
- def macCGHandle ()
- def macQDAlphaHandle ()
- def macQDHandle ()
- def mask ()
- def rect ()
- def save (device[, format=0[, quality=-1]])
- def save (fileName[, format=0[, quality=-1]])
- def scaled (s[, aspectMode=Qt.IgnoreAspectRatio[, mode=Qt.FastTransformation]])
- def scaled (w, h[, aspectMode=Qt.IgnoreAspectRatio[, mode=Qt.FastTransformation]])
- def scaledToHeight (h[, mode=Qt.FastTransformation])
- def scaledToWidth (w[, mode=Qt.FastTransformation])
- def scroll (dx, dy, rect[, exposed=0])
- def scroll (dx, dy, x, y, width, height[, exposed=0])
- def setAlphaChannel (arg__1)
- def setMask (arg__1)
- def size ()
- def swap (other)
- def toImage ()
- def transformed (arg__1[, mode=Qt.FastTransformation])
- def transformed (arg__1[, mode=Qt.FastTransformation])
Static functions¶
- def defaultDepth ()
- def fromImage (image[, flags=Qt.AutoColor])
- def fromImageReader (imageReader[, flags=Qt.AutoColor])
- def grabWidget (widget, rect)
- def grabWidget (widget[, x=0[, y=0[, w=-1[, h=-1]]]])
- def grabWindow (arg__1[, x=0[, y=0[, w=-1[, h=-1]]]])
- def trueMatrix (m, w, h)
- def trueMatrix (m, w, h)
Detailed Description¶
The PySide.QtGui.QPixmap class is an off-screen image representation that can be used as a paint device.
Qt provides four classes for handling image data: PySide.QtGui.QImage , PySide.QtGui.QPixmap , PySide.QtGui.QBitmap and PySide.QtGui.QPicture . PySide.QtGui.QImage is designed and optimized for I/O, and for direct pixel access and manipulation, while PySide.QtGui.QPixmap is designed and optimized for showing images on screen. PySide.QtGui.QBitmap is only a convenience class that inherits PySide.QtGui.QPixmap , ensuring a depth of 1. The PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.isQBitmap() function returns true if a PySide.QtGui.QPixmap object is really a bitmap, otherwise returns false. Finally, the PySide.QtGui.QPicture class is a paint device that records and replays PySide.QtGui.QPainter commands.
A PySide.QtGui.QPixmap can easily be displayed on the screen using PySide.QtGui.QLabel or one of PySide.QtGui.QAbstractButton ‘s subclasses (such as PySide.QtGui.QPushButton and PySide.QtGui.QToolButton ). PySide.QtGui.QLabel has a pixmap property, whereas PySide.QtGui.QAbstractButton has an icon property.
In addition to the ordinary constructors, a PySide.QtGui.QPixmap can be constructed using the static PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.grabWidget() and PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.grabWindow() functions which creates a PySide.QtGui.QPixmap and paints the given widget, or window, into it.
PySide.QtGui.QPixmap objects can be passed around by value since the PySide.QtGui.QPixmap class uses implicit data sharing. For more information, see the Implicit Data Sharing documentation. PySide.QtGui.QPixmap objects can also be streamed.
Note that the pixel data in a pixmap is internal and is managed by the underlying window system. Because PySide.QtGui.QPixmap is a PySide.QtGui.QPaintDevice subclass, PySide.QtGui.QPainter can be used to draw directly onto pixmaps. Pixels can only be accessed through PySide.QtGui.QPainter functions or by converting the PySide.QtGui.QPixmap to a PySide.QtGui.QImage . However, the PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.fill() function is available for initializing the entire pixmap with a given color.
There are functions to convert between PySide.QtGui.QImage and PySide.QtGui.QPixmap . Typically, the PySide.QtGui.QImage class is used to load an image file, optionally manipulating the image data, before the PySide.QtGui.QImage object is converted into a PySide.QtGui.QPixmap to be shown on screen. Alternatively, if no manipulation is desired, the image file can be loaded directly into a PySide.QtGui.QPixmap . On Windows, the PySide.QtGui.QPixmap class also supports conversion between HBITMAP and PySide.QtGui.QPixmap . On Symbian, the PySide.QtGui.QPixmap class also supports conversion between CFbsBitmap and PySide.QtGui.QPixmap .
PySide.QtGui.QPixmap provides a collection of functions that can be used to obtain a variety of information about the pixmap. In addition, there are several functions that enables transformation of the pixmap.
Reading and Writing Image Files¶
PySide.QtGui.QPixmap provides several ways of reading an image file: The file can be loaded when constructing the PySide.QtGui.QPixmap object, or by using the PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.load() or PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.loadFromData() functions later on. When loading an image, the file name can either refer to an actual file on disk or to one of the application’s embedded resources. See The Qt Resource System overview for details on how to embed images and other resource files in the application’s executable.
Simply call the PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.save() function to save a PySide.QtGui.QPixmap object.
The complete list of supported file formats are available through the QImageReader.supportedImageFormats() and QImageWriter.supportedImageFormats() functions. New file formats can be added as plugins. By default, Qt supports the following formats:
Format Description Qt’s support BMP Windows Bitmap Read/write GIF Graphic Interchange Format (optional) Read JPG Joint Photographic Experts Group Read/write JPEG Joint Photographic Experts Group Read/write PNG Portable Network Graphics Read/write PBM Portable Bitmap Read PGM Portable Graymap Read PPM Portable Pixmap Read/write XBM X11 Bitmap Read/write XPM X11 Pixmap Read/write
Pixmap Information¶
PySide.QtGui.QPixmap provides a collection of functions that can be used to obtain a variety of information about the pixmap:
Available Functions Geometry The PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.size() , PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.width() and PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.height() functions provide information about the pixmap’s size. The PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.rect() function returns the image’s enclosing rectangle. Alpha component The PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.hasAlphaChannel() returns true if the pixmap has a format that respects the alpha channel, otherwise returns false. The PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.hasAlpha() , PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.setMask() and PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.mask() functions are legacy and should not be used. They are potentially very slow.
The PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.createHeuristicMask() function creates and returns a 1-bpp heuristic mask (i.e. a PySide.QtGui.QBitmap ) for this pixmap. It works by selecting a color from one of the corners and then chipping away pixels of that color, starting at all the edges. The PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.createMaskFromColor() function creates and returns a mask (i.e. a PySide.QtGui.QBitmap ) for the pixmap based on a given color.Low-level information The PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.depth() function returns the depth of the pixmap. The PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.defaultDepth() function returns the default depth, i.e. the depth used by the application on the given screen.
The PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.cacheKey() function returns a number that uniquely identifies the contents of the PySide.QtGui.QPixmap object.
The x11Info() function returns information about the configuration of the X display used by the screen to which the pixmap currently belongs. The x11PictureHandle() function returns the X11 Picture handle of the pixmap for XRender support. Note that the two latter functions are only available on x11.
Pixmap Conversion¶
A PySide.QtGui.QPixmap object can be converted into a PySide.QtGui.QImage using the PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.toImage() function. Likewise, a PySide.QtGui.QImage can be converted into a PySide.QtGui.QPixmap using the PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.fromImage() . If this is too expensive an operation, you can use QBitmap.fromImage() instead.
In addition, on Windows, the PySide.QtGui.QPixmap class supports conversion to and from HBITMAP: the toWinHBITMAP() function creates a HBITMAP equivalent to the PySide.QtGui.QPixmap , based on the given QPixmap.HBitmapFormat , and returns the HBITMAP handle. The fromWinHBITMAP() function returns a PySide.QtGui.QPixmap that is equivalent to the given bitmap which has the specified format. The PySide.QtGui.QPixmap class also supports conversion to and from HICON: the toWinHICON() function creates a HICON equivalent to the PySide.QtGui.QPixmap , and returns the HICON handle. The fromWinHICON() function returns a PySide.QtGui.QPixmap that is equivalent to the given icon.
In addition, on Symbian, the PySide.QtGui.QPixmap class supports conversion to and from CFbsBitmap: the toSymbianCFbsBitmap() function creates CFbsBitmap equivalent to the PySide.QtGui.QPixmap , based on given mode and returns a CFbsBitmap object. The fromSymbianCFbsBitmap() function returns a PySide.QtGui.QPixmap that is equivalent to the given bitmap and given mode.
Pixmap Transformations¶
PySide.QtGui.QPixmap supports a number of functions for creating a new pixmap that is a transformed version of the original:
The PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.scaled() , PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.scaledToWidth() and PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.scaledToHeight() functions return scaled copies of the pixmap, while the PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.copy() function creates a PySide.QtGui.QPixmap that is a plain copy of the original one.
The PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.transformed() function returns a copy of the pixmap that is transformed with the given transformation matrix and transformation mode: Internally, the transformation matrix is adjusted to compensate for unwanted translation, i.e. PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.transformed() returns the smallest pixmap containing all transformed points of the original pixmap. The static PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.trueMatrix() function returns the actual matrix used for transforming the pixmap.
Note
When using the native X11 graphics system, the pixmap becomes invalid when the PySide.QtGui.QApplication instance is destroyed.
- class PySide.QtGui.QPixmap¶
- class PySide.QtGui.QPixmap(image)
- class PySide.QtGui.QPixmap(arg__1)
- class PySide.QtGui.QPixmap(arg__1)
- class PySide.QtGui.QPixmap(fileName[, format=0[, flags=Qt.AutoColor]])
- class PySide.QtGui.QPixmap(xpm)
- class PySide.QtGui.QPixmap(w, h)
Parameters: - w – PySide.QtCore.int
- flags – PySide.QtCore.Qt.ImageConversionFlags
- h – PySide.QtCore.int
- image – PySide.QtGui.QImage
- format – str
- fileName – unicode
- arg__1 – PySide.QtGui.QPixmap
- xpm – PySide.QtCore.char
Constructs a null pixmap.
See also
Constructs a pixmap that is a copy of the given pixmap .
See also
This is an overloaded function.
Constructs a pixmap of the given size .
Warning
This will create a PySide.QtGui.QPixmap with uninitialized data. Call PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.fill() to fill the pixmap with an appropriate color before drawing onto it with PySide.QtGui.QPainter .
Constructs a pixmap with the given width and height . If either width or height is zero, a null pixmap is constructed.
Warning
This will create a PySide.QtGui.QPixmap with uninitialized data. Call PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.fill() to fill the pixmap with an appropriate color before drawing onto it with PySide.QtGui.QPainter .
See also
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.Type¶
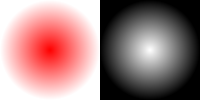
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.alphaChannel()¶
Return type: PySide.QtGui.QPixmap Returns the alpha channel of the pixmap as a new grayscale PySide.QtGui.QPixmap in which each pixel’s red, green, and blue values are given the alpha value of the original pixmap. The color depth of the returned pixmap is the system depth on X11 and 8-bit on Windows and Mac OS X.
You can use this function while debugging to get a visible image of the alpha channel. If the pixmap doesn’t have an alpha channel, i.e., the alpha channel’s value for all pixels equals 0xff), a null pixmap is returned. You can check this with the isNull() function.
We show an example:
pixmap = QPixmap(100, 100) pixmap.fill(Qt.transparent) gradient = QRadialGradient(50, 50, 50, 50, 50) gradient.setColorAt(0, QColor.fromRgbF(1, 0, 0, 1)) gradient.setColorAt(1, QColor.fromRgbF(0, 0, 0, 0)) painter = QPainter(pixmap) painter.fillRect(0, 0, 100, 100, gradient) channelImage = pixmap.alphaChannel() update()
Warning
This is an expensive operation. The alpha channel of the pixmap is extracted dynamically from the pixeldata. Most usecases of this function are covered by PySide.QtGui.QPainter and compositionModes which will normally execute faster.
See also
PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.setAlphaChannel() Pixmap Information
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.cacheKey()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.qint64 Returns a number that identifies this PySide.QtGui.QPixmap . Distinct PySide.QtGui.QPixmap objects can only have the same cache key if they refer to the same contents.
The PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.cacheKey() will change when the pixmap is altered.
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.convertFromImage(img[, flags=Qt.AutoColor])¶
Parameters: - img – PySide.QtGui.QImage
- flags – PySide.QtCore.Qt.ImageConversionFlags
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.copy(x, y, width, height)¶
Parameters: - x – PySide.QtCore.int
- y – PySide.QtCore.int
- width – PySide.QtCore.int
- height – PySide.QtCore.int
Return type: This is an overloaded function.
Returns a deep copy of the subset of the pixmap that is specified by the rectangle PySide.QtCore.QRect ( x , y , width , height ).
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.copy([rect=QRect()])
Parameters: rect – PySide.QtCore.QRect Return type: PySide.QtGui.QPixmap Returns a deep copy of the subset of the pixmap that is specified by the given rectangle . For more information on deep copies, see the Implicit Data Sharing documentation.
If the given rectangle is empty, the whole image is copied.
See also
PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.operator=() PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.QPixmap() Pixmap Transformations
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.createHeuristicMask([clipTight=true])¶
Parameters: clipTight – PySide.QtCore.bool Return type: PySide.QtGui.QBitmap Creates and returns a heuristic mask for this pixmap.
The function works by selecting a color from one of the corners and then chipping away pixels of that color, starting at all the edges. If clipTight is true (the default) the mask is just large enough to cover the pixels; otherwise, the mask is larger than the data pixels.
The mask may not be perfect but it should be reasonable, so you can do things such as the following:
myPixmap = QPixmap() myPixmap.setMask(myPixmap.createHeuristicMask())
This function is slow because it involves converting to/from a PySide.QtGui.QImage , and non-trivial computations.
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.createMaskFromColor(maskColor, mode)¶
Parameters: - maskColor – PySide.QtGui.QColor
- mode – PySide.QtCore.Qt.MaskMode
Return type:
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.createMaskFromColor(maskColor)
Parameters: maskColor – PySide.QtGui.QColor Return type: PySide.QtGui.QBitmap This is an overloaded function.
Creates and returns a mask for this pixmap based on the given maskColor . Same as calling createMaskFromColor(maskColor, Qt.MaskInColor )
- static PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.defaultDepth()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.int Returns the default pixmap depth used by the application.
On Windows and Mac, the default depth is always 32. On X11 and embedded, the depth of the screen will be returned by this function.
See also
PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.depth() QColormap.depth() Pixmap Information
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.deref()¶
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.doImageIO(io, quality)¶
Parameters: - io – PySide.QtGui.QImageWriter
- quality – PySide.QtCore.int
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.fill(widget, xofs, yofs)¶
Parameters: - widget – PySide.QtGui.QWidget
- xofs – PySide.QtCore.int
- yofs – PySide.QtCore.int
This is an overloaded function.
Fills the pixmap with the widget ‘s background color or pixmap. The given point, (x , y ), defines an offset in widget coordinates to which the pixmap’s top-left pixel will be mapped to.
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.fill(widget, ofs)
Parameters: - widget – PySide.QtGui.QWidget
- ofs – PySide.QtCore.QPoint
Fills the pixmap with the widget ‘s background color or pixmap according to the given offset.
The PySide.QtCore.QPoint offset defines a point in widget coordinates to which the pixmap’s top-left pixel will be mapped to. This is only significant if the widget has a background pixmap; otherwise the pixmap will simply be filled with the background color of the widget.
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.fill([fillColor=Qt.white])
Parameters: fillColor – PySide.QtGui.QColor Fills the pixmap with the given color .
The effect of this function is undefined when the pixmap is being painted on.
See also
Pixmap Transformations
- static PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.fromImage(image[, flags=Qt.AutoColor])¶
Parameters: - image – PySide.QtGui.QImage
- flags – PySide.QtCore.Qt.ImageConversionFlags
Return type:
- static PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.fromImageReader(imageReader[, flags=Qt.AutoColor])¶
Parameters: - imageReader – PySide.QtGui.QImageReader
- flags – PySide.QtCore.Qt.ImageConversionFlags
Return type:
- static PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.grabWidget(widget[, x=0[, y=0[, w=-1[, h=-1]]]])¶
Parameters: - widget – PySide.QtGui.QWidget
- x – PySide.QtCore.int
- y – PySide.QtCore.int
- w – PySide.QtCore.int
- h – PySide.QtCore.int
Return type: This is an overloaded function.
Creates a pixmap and paints the given widget , restricted by PySide.QtCore.QRect (x , y , width , height ), in it.
Warning
Do not grab a widget from its QWidget.paintEvent() . However, it is safe to grab a widget from another widget’s PySide.QtGui.QWidget.paintEvent() .
- static PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.grabWidget(widget, rect)
Parameters: - widget – PySide.QtGui.QWidget
- rect – PySide.QtCore.QRect
Return type: Creates a pixmap and paints the given widget , restricted by the given rectangle , in it. If the widget has any children, then they are also painted in the appropriate positions.
If no rectangle is specified (the default) the entire widget is painted.
If widget is 0, the specified rectangle doesn’t overlap the widget’s rectangle, or an error occurs, the function will return a null PySide.QtGui.QPixmap . If the rectangle is a superset of the given widget , the areas outside the widget are covered with the widget’s background.
This function actually asks widget to paint itself (and its children to paint themselves) by calling paintEvent() with painter redirection turned on. But PySide.QtGui.QPixmap also provides the PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.grabWindow() function which is a bit faster by grabbing pixels directly off the screen. In addition, if there are overlaying windows, PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.grabWindow() , unlike PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.grabWidget() , will see them.
Warning
Do not grab a widget from its QWidget.paintEvent() . However, it is safe to grab a widget from another widget’s PySide.QtGui.QWidget.paintEvent() .
See also
- static PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.grabWindow(arg__1[, x=0[, y=0[, w=-1[, h=-1]]]])¶
Parameters: - arg__1 – PySide.QtCore.long
- x – PySide.QtCore.int
- y – PySide.QtCore.int
- w – PySide.QtCore.int
- h – PySide.QtCore.int
Return type:
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.hasAlpha()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool Returns true if this pixmap has an alpha channel, or has a mask, otherwise returns false.
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.hasAlphaChannel()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool Returns true if the pixmap has a format that respects the alpha channel, otherwise returns false.
See also
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.init(arg__1, arg__2, arg__3)¶
Parameters: - arg__1 – PySide.QtCore.int
- arg__2 – PySide.QtCore.int
- arg__3 – PySide.QtCore.int
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.init(arg__1, arg__2[, arg__3=PixmapType])
Parameters: - arg__1 – PySide.QtCore.int
- arg__2 – PySide.QtCore.int
- arg__3 – QPixmap.Type
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.isNull()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool Returns true if this is a null pixmap; otherwise returns false.
A null pixmap has zero width, zero height and no contents. You cannot draw in a null pixmap.
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.isQBitmap()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool Returns true if this is a PySide.QtGui.QBitmap ; otherwise returns false.
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.load(fileName[, format=0[, flags=Qt.AutoColor]])¶
Parameters: - fileName – unicode
- format – str
- flags – PySide.QtCore.Qt.ImageConversionFlags
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.loadFromData(buf[, format=0[, flags=Qt.AutoColor]])¶
Parameters: - buf – PySide.QtCore.uchar
- format – str
- flags – PySide.QtCore.Qt.ImageConversionFlags
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.loadFromData(data[, format=0[, flags=Qt.AutoColor]])
Parameters: - data – PySide.QtCore.QByteArray
- format – str
- flags – PySide.QtCore.Qt.ImageConversionFlags
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.macCGHandle()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.Qt::HANDLE
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.macQDAlphaHandle()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.Qt::HANDLE
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.macQDHandle()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.Qt::HANDLE
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.mask()¶
Return type: PySide.QtGui.QBitmap Extracts a bitmap mask from the pixmap’s alpha channel.
Warning
This is potentially an expensive operation. The mask of the pixmap is extracted dynamically from the pixeldata.
See also
PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.setMask() Pixmap Information
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.rect()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.QRect Returns the pixmap’s enclosing rectangle.
See also
Pixmap Information
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.save(fileName[, format=0[, quality=-1]])¶
Parameters: - fileName – unicode
- format – str
- quality – PySide.QtCore.int
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool
Saves the pixmap to the file with the given fileName using the specified image file format and quality factor. Returns true if successful; otherwise returns false.
The quality factor must be in the range [0,100] or -1. Specify 0 to obtain small compressed files, 100 for large uncompressed files, and -1 to use the default settings.
If format is 0, an image format will be chosen from fileName ‘s suffix.
See also
Reading and Writing Image Files
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.save(device[, format=0[, quality=-1]])
Parameters: - device – PySide.QtCore.QIODevice
- format – str
- quality – PySide.QtCore.int
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool
This is an overloaded function.
This function writes a PySide.QtGui.QPixmap to the given device using the specified image file format and quality factor. This can be used, for example, to save a pixmap directly into a PySide.QtCore.QByteArray :
pixmap = QPixmap() bytes = QByteArray() buffer(bytes) buffer.open(QIODevice.WriteOnly) pixmap.save(buffer, "PNG") # writes pixmap into bytes in PNG format
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.scaled(w, h[, aspectMode=Qt.IgnoreAspectRatio[, mode=Qt.FastTransformation]])¶
Parameters: - w – PySide.QtCore.int
- h – PySide.QtCore.int
- aspectMode – PySide.QtCore.Qt.AspectRatioMode
- mode – PySide.QtCore.Qt.TransformationMode
Return type:
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.scaled(s[, aspectMode=Qt.IgnoreAspectRatio[, mode=Qt.FastTransformation]])
Parameters: - s – PySide.QtCore.QSize
- aspectMode – PySide.QtCore.Qt.AspectRatioMode
- mode – PySide.QtCore.Qt.TransformationMode
Return type:
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.scaledToHeight(h[, mode=Qt.FastTransformation])¶
Parameters: - h – PySide.QtCore.int
- mode – PySide.QtCore.Qt.TransformationMode
Return type:
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.scaledToWidth(w[, mode=Qt.FastTransformation])¶
Parameters: - w – PySide.QtCore.int
- mode – PySide.QtCore.Qt.TransformationMode
Return type:
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.scroll(dx, dy, rect[, exposed=0])¶
Parameters: - dx – PySide.QtCore.int
- dy – PySide.QtCore.int
- rect – PySide.QtCore.QRect
- exposed – PySide.QtGui.QRegion
Scrolls the area rect of this pixmap by (dx , dy ). The exposed region is left unchanged. You can optionally pass a pointer to an empty PySide.QtGui.QRegion to get the region that is exposed by the scroll operation.
pixmap = QPixmap("background.png") exposed = QRegion() pixmap.scroll(10, 10, pixmap.rect(), exposed)
You cannot scroll while there is an active painter on the pixmap.
See also
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.scroll(dx, dy, x, y, width, height[, exposed=0])
Parameters: - dx – PySide.QtCore.int
- dy – PySide.QtCore.int
- x – PySide.QtCore.int
- y – PySide.QtCore.int
- width – PySide.QtCore.int
- height – PySide.QtCore.int
- exposed – PySide.QtGui.QRegion
This convenience function is equivalent to calling QPixmap::scroll(dx , dy , PySide.QtCore.QRect (x , y , width , height ), exposed ).
See also
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.setAlphaChannel(arg__1)¶
Parameters: arg__1 – PySide.QtGui.QPixmap Sets the alpha channel of this pixmap to the given alphaChannel by converting the alphaChannel into 32 bit and using the intensity of the RGB pixel values.
The effect of this function is undefined when the pixmap is being painted on.
Warning
This is potentially an expensive operation. Most usecases for this function are covered by PySide.QtGui.QPainter and compositionModes which will normally execute faster.
See also
PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.alphaChannel() Pixmap Transformations
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.setMask(arg__1)¶
Parameters: arg__1 – PySide.QtGui.QBitmap Sets a mask bitmap.
This function merges the mask with the pixmap’s alpha channel. A pixel value of 1 on the mask means the pixmap’s pixel is unchanged; a value of 0 means the pixel is transparent. The mask must have the same size as this pixmap.
Setting a null mask resets the mask, leaving the previously transparent pixels black. The effect of this function is undefined when the pixmap is being painted on.
Warning
This is potentially an expensive operation.
See also
PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.mask() Pixmap Transformations PySide.QtGui.QBitmap
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.size()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.QSize Returns the size of the pixmap.
See also
PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.width() PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.height() Pixmap Information
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.swap(other)¶
Parameters: other – PySide.QtGui.QPixmap Swaps pixmap other with this pixmap. This operation is very fast and never fails.
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.toImage()¶
Return type: PySide.QtGui.QImage Converts the pixmap to a PySide.QtGui.QImage . Returns a null image if the conversion fails.
If the pixmap has 1-bit depth, the returned image will also be 1 bit deep. Images with more bits will be returned in a format closely represents the underlying system. Usually this will be QImage.Format_ARGB32_Premultiplied for pixmaps with an alpha and QImage.Format_RGB32 or QImage.Format_RGB16 for pixmaps without alpha.
Note that for the moment, alpha masks on monochrome images are ignored.
See also
PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.fromImage() Image Formats
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.transformed(arg__1[, mode=Qt.FastTransformation])¶
Parameters: - arg__1 – PySide.QtGui.QTransform
- mode – PySide.QtCore.Qt.TransformationMode
Return type:
- PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.transformed(arg__1[, mode=Qt.FastTransformation])
Parameters: - arg__1 – PySide.QtGui.QMatrix
- mode – PySide.QtCore.Qt.TransformationMode
Return type:
- static PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.trueMatrix(m, w, h)¶
Parameters: - m – PySide.QtGui.QTransform
- w – PySide.QtCore.int
- h – PySide.QtCore.int
Return type: Returns the actual matrix used for transforming a pixmap with the given width , height and matrix .
When transforming a pixmap using the PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.transformed() function, the transformation matrix is internally adjusted to compensate for unwanted translation, i.e. PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.transformed() returns the smallest pixmap containing all transformed points of the original pixmap. This function returns the modified matrix, which maps points correctly from the original pixmap into the new pixmap.
See also
PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.transformed() Pixmap Transformations
- static PySide.QtGui.QPixmap.trueMatrix(m, w, h)
Parameters: - m – PySide.QtGui.QMatrix
- w – PySide.QtCore.int
- h – PySide.QtCore.int
Return type: This is an overloaded function.
This convenience function loads the matrix m into a PySide.QtGui.QTransform and calls the overloaded function with the PySide.QtGui.QTransform and the width w and the height h .




