QTextBlock¶
Synopsis¶
Functions¶
- def __eq__ (o)
- def __iter__ ()
- def __lt__ (o)
- def __ne__ (o)
- def begin ()
- def blockFormat ()
- def blockFormatIndex ()
- def blockNumber ()
- def charFormat ()
- def charFormatIndex ()
- def clearLayout ()
- def contains (position)
- def document ()
- def end ()
- def firstLineNumber ()
- def fragmentIndex ()
- def isValid ()
- def isVisible ()
- def layout ()
- def length ()
- def lineCount ()
- def next ()
- def position ()
- def previous ()
- def revision ()
- def setLineCount (count)
- def setRevision (rev)
- def setUserData (data)
- def setUserState (state)
- def setVisible (visible)
- def text ()
- def textDirection ()
- def textList ()
- def userData ()
- def userState ()
Detailed Description¶
The PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock class provides a container for text fragments in a PySide.QtGui.QTextDocument .
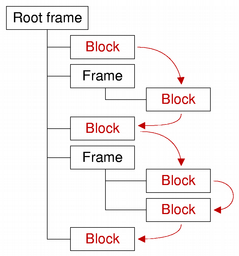
A text block encapsulates a block or paragraph of text in a PySide.QtGui.QTextDocument . PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock provides read-only access to the block/paragraph structure of QTextDocuments. It is mainly of use if you want to implement your own layouts for the visual representation of a PySide.QtGui.QTextDocument , or if you want to iterate over a document and write out the contents in your own custom format.
Text blocks are created by their parent documents. If you need to create a new text block, or modify the contents of a document while examining its contents, use the cursor-based interface provided by PySide.QtGui.QTextCursor instead.
Each text block is located at a specific PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.position() in a PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.document() . The contents of the block can be obtained by using the PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.text() function. The PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.length() function determines the block’s size within the document (including formatting characters). The visual properties of the block are determined by its text PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.layout() , its PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.charFormat() , and its PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.blockFormat() .
The PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.next() and PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.previous() functions enable iteration over consecutive valid blocks in a document under the condition that the document is not modified by other means during the iteration process. Note that, although blocks are returned in sequence, adjacent blocks may come from different places in the document structure. The validity of a block can be determined by calling PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.isValid() .
PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock provides comparison operators to make it easier to work with blocks: PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.operator==() compares two block for equality, PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.operator!=() compares two blocks for inequality, and PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.operator<() determines whether a block precedes another in the same document.
- class PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock¶
- class PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock(o)
Parameters: o – PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock Copies the other text block’s attributes to this text block.
- PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.__iter__()¶
Return type: PyObject
- PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.begin()¶
Return type: PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock::iterator Returns a text block iterator pointing to the beginning of the text block.
See also
- PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.blockFormat()¶
Return type: PySide.QtGui.QTextBlockFormat Returns the PySide.QtGui.QTextBlockFormat that describes block-specific properties.
See also
- PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.blockFormatIndex()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.int Returns an index into the document’s internal list of block formats for the text block’s format.
See also
- PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.blockNumber()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.int Returns the number of this block, or -1 if the block is invalid.
See also
- PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.charFormat()¶
Return type: PySide.QtGui.QTextCharFormat Returns the PySide.QtGui.QTextCharFormat that describes the block’s character format. The block’s character format is used when inserting text into an empty block.
- PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.charFormatIndex()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.int Returns an index into the document’s internal list of character formats for the text block’s character format.
See also
- PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.clearLayout()¶
Clears the PySide.QtGui.QTextLayout that is used to lay out and display the block’s contents.
See also
- PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.contains(position)¶
Parameters: position – PySide.QtCore.int Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool Returns true if the given position is located within the text block; otherwise returns false.
- PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.document()¶
Return type: PySide.QtGui.QTextDocument Returns the text document this text block belongs to, or 0 if the text block does not belong to any document.
- PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.end()¶
Return type: PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock::iterator Returns a text block iterator pointing to the end of the text block.
- PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.firstLineNumber()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.int Returns the first line number of this block, or -1 if the block is invalid. Unless the layout supports it, the line number is identical to the block number.
See also
- PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.fragmentIndex()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.int
- PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.isValid()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool Returns true if this text block is valid; otherwise returns false.
- PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.isVisible()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool Returns true if the block is visible; otherwise returns false.
See also
- PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.layout()¶
Return type: PySide.QtGui.QTextLayout Returns the PySide.QtGui.QTextLayout that is used to lay out and display the block’s contents.
Note that the returned PySide.QtGui.QTextLayout object can only be modified from the documentChanged implementation of a PySide.QtGui.QAbstractTextDocumentLayout subclass. Any changes applied from the outside cause undefined behavior.
- PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.length()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.int Returns the length of the block in characters.
Note
The length returned includes all formatting characters, for example, newline.
- PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.lineCount()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.int Returns the line count. Not all document layouts support this feature.
- PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.next()¶
Return type: PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock Returns the text block in the document after this block, or an empty text block if this is the last one.
Note that the next block may be in a different frame or table to this block.
- PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.__ne__(o)¶
Parameters: o – PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool Returns true if this text block is different from the other text block.
- PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.__lt__(o)¶
Parameters: o – PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool Returns true if this text block occurs before the other text block in the document.
- PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.__eq__(o)¶
Parameters: o – PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool Returns true if this text block is the same as the other text block.
- PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.position()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.int Returns the index of the block’s first character within the document.
- PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.previous()¶
Return type: PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock Returns the text block in the document before this block, or an empty text block if this is the first one.
Note that the next block may be in a different frame or table to this block.
- PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.revision()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.int Returns the blocks revision.
- PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.setLineCount(count)¶
Parameters: count – PySide.QtCore.int Sets the line count to count .
See also
- PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.setRevision(rev)¶
Parameters: rev – PySide.QtCore.int Sets a blocks revision to rev .
- PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.setUserData(data)¶
Parameters: data – PySide.QtGui.QTextBlockUserData Attaches the given data object to the text block.
PySide.QtGui.QTextBlockUserData can be used to store custom settings. The ownership is passed to the underlying text document, i.e. the provided PySide.QtGui.QTextBlockUserData object will be deleted if the corresponding text block gets deleted. The user data object is not stored in the undo history, so it will not be available after undoing the deletion of a text block.
For example, if you write a programming editor in an IDE, you may want to let your user set breakpoints visually in your code for an integrated debugger. In a programming editor a line of text usually corresponds to one PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock . The PySide.QtGui.QTextBlockUserData interface allows the developer to store data for each PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock , like for example in which lines of the source code the user has a breakpoint set. Of course this could also be stored externally, but by storing it inside the PySide.QtGui.QTextDocument , it will for example be automatically deleted when the user deletes the associated line. It’s really just a way to store custom information in the PySide.QtGui.QTextDocument without using custom properties in PySide.QtGui.QTextFormat which would affect the undo/redo stack.
See also
- PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.setUserState(state)¶
Parameters: state – PySide.QtCore.int Stores the specified state integer value in the text block. This may be useful for example in a syntax highlighter to store a text parsing state.
See also
- PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.setVisible(visible)¶
Parameters: visible – PySide.QtCore.bool Sets the block’s visibility to visible .
See also
- PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.text()¶
Return type: unicode Returns the block’s contents as plain text.
- PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.textDirection()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.Qt.LayoutDirection Returns the resolved text direction.
If the block has no explicit direction set, it will resolve the direction from the blocks content. Returns either Qt.LeftToRight or Qt.RightToLeft .
See also
QTextFormat.layoutDirection() QString.isRightToLeft() Qt.LayoutDirection
- PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.textList()¶
Return type: PySide.QtGui.QTextList If the block represents a list item, returns the list that the item belongs to; otherwise returns 0.
- PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.userData()¶
Return type: PySide.QtGui.QTextBlockUserData Returns a pointer to a PySide.QtGui.QTextBlockUserData object if previously set with PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.setUserData() or a null pointer.
- PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.userState()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.int Returns the integer value previously set with PySide.QtGui.QTextBlock.setUserState() or -1.




