QMdiArea¶
Synopsis¶
Functions¶
- def activationOrder ()
- def activeSubWindow ()
- def addSubWindow (widget[, flags=0])
- def background ()
- def currentSubWindow ()
- def documentMode ()
- def removeSubWindow (widget)
- def setActivationOrder (order)
- def setBackground (background)
- def setDocumentMode (enabled)
- def setOption (option[, on=true])
- def setTabPosition (position)
- def setTabShape (shape)
- def setTabsClosable (closable)
- def setTabsMovable (movable)
- def setViewMode (mode)
- def subWindowList ([order=CreationOrder])
- def tabPosition ()
- def tabShape ()
- def tabsClosable ()
- def tabsMovable ()
- def testOption (opton)
- def viewMode ()
Slots¶
- def activateNextSubWindow ()
- def activatePreviousSubWindow ()
- def cascadeSubWindows ()
- def closeActiveSubWindow ()
- def closeAllSubWindows ()
- def setActiveSubWindow (window)
- def tileSubWindows ()
Signals¶
- def subWindowActivated (arg__1)
Detailed Description¶
The PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea widget provides an area in which MDI windows are displayed.
PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea functions, essentially, like a window manager for MDI windows. For instance, it draws the windows it manages on itself and arranges them in a cascading or tile pattern. PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea is commonly used as the center widget in a PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow to create MDI applications, but can also be placed in any layout. The following code adds an area to a main window:
mainWindow = QMainWindow() mainWindow.setCentralWidget(mdiArea)Unlike the window managers for top-level windows, all window flags ( Qt.WindowFlags ) are supported by PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea as long as the flags are supported by the current widget style. If a specific flag is not supported by the style (e.g., the WindowShadeButtonHint ), you can still shade the window with showShaded().
Subwindows in PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea are instances of PySide.QtGui.QMdiSubWindow . They are added to an MDI area with PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.addSubWindow() . It is common to pass a PySide.QtGui.QWidget , which is set as the internal widget, to this function, but it is also possible to pass a PySide.QtGui.QMdiSubWindow directly.The class inherits PySide.QtGui.QWidget , and you can use the same API as with a normal top-level window when programming. PySide.QtGui.QMdiSubWindow also has behavior that is specific to MDI windows. See the PySide.QtGui.QMdiSubWindow class description for more details.
A subwindow becomes active when it gets the keyboard focus, or when PySide.QtGui.QWidget.setFocus() is called. The user activates a window by moving focus in the usual ways. The MDI area emits the PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.subWindowActivated() signal when the active window changes, and the PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.activeSubWindow() function returns the active subwindow.
The convenience function PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.subWindowList() returns a list of all subwindows. This information could be used in a popup menu containing a list of windows, for example.
The subwindows are sorted by the current QMdiArea.WindowOrder . This is used for the PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.subWindowList() and for PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.activateNextSubWindow() and acivatePreviousSubWindow(). Also, it is used when cascading or tiling the windows with PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.cascadeSubWindows() and PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.tileSubWindows() .
PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea provides two built-in layout strategies for subwindows: PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.cascadeSubWindows() and PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.tileSubWindows() . Both are slots and are easily connected to menu entries.
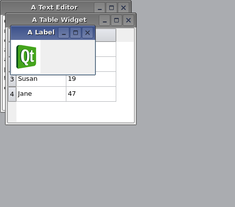
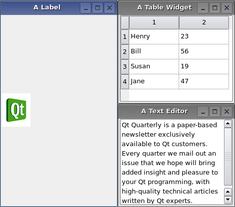
Note
The default scroll bar property for PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea is Qt.ScrollBarAlwaysOff .
See also
- class PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea([parent=None])¶
Parameters: parent – PySide.QtGui.QWidget Constructs an empty mdi area. parent is passed to PySide.QtGui.QWidget ‘s constructor.
- PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.WindowOrder¶
Specifies the criteria to use for ordering the list of child windows returned by PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.subWindowList() . The functions PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.cascadeSubWindows() and PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.tileSubWindows() follow this order when arranging the windows.
Constant Description QMdiArea.CreationOrder The windows are returned in the order of their creation. QMdiArea.StackingOrder The windows are returned in the order in which they are stacked, with the top-most window being last in the list. QMdiArea.ActivationHistoryOrder The windows are returned in the order in which they were activated.
- PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.ViewMode¶
This enum describes the view mode of the area; i.e. how sub-windows will be displayed.
Constant Description QMdiArea.SubWindowView Display sub-windows with window frames (default). QMdiArea.TabbedView Display sub-windows with tabs in a tab bar. See also
- PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.AreaOption¶
This enum describes options that customize the behavior of the PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea .
Constant Description QMdiArea.DontMaximizeSubWindowOnActivation When the active subwindow is maximized, the default behavior is to maximize the next subwindow that is activated. Set this option if you do not want this behavior.
- PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.activateNextSubWindow()¶
Gives the keyboard focus to another window in the list of child windows. The window activated will be the next one determined by the current activation order .
See also
PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.activatePreviousSubWindow() QMdiArea.WindowOrder
- PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.activatePreviousSubWindow()¶
Gives the keyboard focus to another window in the list of child windows. The window activated will be the previous one determined by the current activation order .
See also
PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.activateNextSubWindow() QMdiArea.WindowOrder
- PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.activationOrder()¶
Return type: PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.WindowOrder This property holds the ordering criteria for subwindow lists.
This property specifies the ordering criteria for the list of subwindows returned by PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.subWindowList() . By default, it is the window creation order.
- PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.activeSubWindow()¶
Return type: PySide.QtGui.QMdiSubWindow Returns a pointer to the current active subwindow. If no window is currently active, 0 is returned.
Subwindows are treated as top-level windows with respect to window state, i.e., if a widget outside the MDI area is the active window, no subwindow will be active. Note that if a widget in the window in which the MDI area lives gains focus, the window will be activated.
See also
PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.setActiveSubWindow() Qt.WindowState
- PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.addSubWindow(widget[, flags=0])¶
Parameters: - widget – PySide.QtGui.QWidget
- flags – PySide.QtCore.Qt.WindowFlags
Return type:
- PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.background()¶
Return type: PySide.QtGui.QBrush This property holds the background brush for the workspace.
This property sets the background brush for the workspace area itself. By default, it is a gray color, but can be any brush (e.g., colors, gradients or pixmaps).
- PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.cascadeSubWindows()¶
Arranges all the child windows in a cascade pattern.
- PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.closeActiveSubWindow()¶
Closes the active subwindow.
- PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.closeAllSubWindows()¶
Closes all subwindows by sending a PySide.QtGui.QCloseEvent to each window. You may receive PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.subWindowActivated() signals from subwindows before they are closed (if the MDI area activates the subwindow when another is closing).
Subwindows that ignore the close event will remain open.
- PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.currentSubWindow()¶
Return type: PySide.QtGui.QMdiSubWindow Returns a pointer to the current subwindow, or 0 if there is no current subwindow.
This function will return the same as PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.activeSubWindow() if the PySide.QtGui.QApplication containing PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea is active.
- PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.documentMode()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool This property holds whether the tab bar is set to document mode in tabbed view mode..
Document mode is disabled by default.
- PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.removeSubWindow(widget)¶
Parameters: widget – PySide.QtGui.QWidget Removes widget from the MDI area. The widget must be either a PySide.QtGui.QMdiSubWindow or a widget that is the internal widget of a subwindow. Note widget is never actually deleted by PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea . If a PySide.QtGui.QMdiSubWindow is passed in its parent is set to 0 and it is removed, but if an internal widget is passed in the child widget is set to 0 but the PySide.QtGui.QMdiSubWindow is not removed.
See also
- PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.setActivationOrder(order)¶
Parameters: order – PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.WindowOrder This property holds the ordering criteria for subwindow lists.
This property specifies the ordering criteria for the list of subwindows returned by PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.subWindowList() . By default, it is the window creation order.
- PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.setActiveSubWindow(window)¶
Parameters: window – PySide.QtGui.QMdiSubWindow Activates the subwindow window . If window is 0, any current active window is deactivated.
- PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.setBackground(background)¶
Parameters: background – PySide.QtGui.QBrush This property holds the background brush for the workspace.
This property sets the background brush for the workspace area itself. By default, it is a gray color, but can be any brush (e.g., colors, gradients or pixmaps).
- PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.setDocumentMode(enabled)¶
Parameters: enabled – PySide.QtCore.bool This property holds whether the tab bar is set to document mode in tabbed view mode..
Document mode is disabled by default.
- PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.setOption(option[, on=true])¶
Parameters: - option – PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.AreaOption
- on – PySide.QtCore.bool
If on is true, option is enabled on the MDI area; otherwise it is disabled. See QMdiArea.AreaOption for the effect of each option.
See also
QMdiArea.AreaOption PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.testOption()
- PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.setTabPosition(position)¶
Parameters: position – PySide.QtGui.QTabWidget.TabPosition This property holds the position of the tabs in tabbed view mode..
Possible values for this property are described by the QTabWidget.TabPosition enum.
See also
QTabWidget.TabPosition PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.setViewMode()
- PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.setTabShape(shape)¶
Parameters: shape – PySide.QtGui.QTabWidget.TabShape This property holds the shape of the tabs in tabbed view mode..
Possible values for this property are QTabWidget.Rounded (default) or QTabWidget.Triangular .
See also
QTabWidget.TabShape PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.setViewMode()
- PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.setTabsClosable(closable)¶
Parameters: closable – PySide.QtCore.bool This property holds whether the tab bar should place close buttons on each tab in tabbed view mode..
Tabs are not closable by default.
- PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.setTabsMovable(movable)¶
Parameters: movable – PySide.QtCore.bool This property holds whether the user can move the tabs within the tabbar area in tabbed view mode..
Tabs are not movable by default.
See also
QTabBar.movable PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.setViewMode()
- PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.setViewMode(mode)¶
Parameters: mode – PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.ViewMode This property holds the way sub-windows are displayed in the PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea ..
By default, the SubWindowView is used to display sub-windows.
See also
QMdiArea.ViewMode PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.setTabShape() PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.setTabPosition()
- PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.subWindowActivated(arg__1)¶
Parameters: arg__1 – PySide.QtGui.QMdiSubWindow
- PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.subWindowList([order=CreationOrder])¶
Parameters: order – PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.WindowOrder Return type: Returns a list of all subwindows in the MDI area. If order is CreationOrder (the default), the windows are sorted in the order in which they were inserted into the workspace. If order is StackingOrder , the windows are listed in their stacking order, with the topmost window as the last item in the list. If order is ActivationHistoryOrder , the windows are listed according to their recent activation history.
See also
QMdiArea.WindowOrder
- PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.tabPosition()¶
Return type: PySide.QtGui.QTabWidget.TabPosition This property holds the position of the tabs in tabbed view mode..
Possible values for this property are described by the QTabWidget.TabPosition enum.
See also
QTabWidget.TabPosition PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.setViewMode()
- PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.tabShape()¶
Return type: PySide.QtGui.QTabWidget.TabShape This property holds the shape of the tabs in tabbed view mode..
Possible values for this property are QTabWidget.Rounded (default) or QTabWidget.Triangular .
See also
QTabWidget.TabShape PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.setViewMode()
- PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.tabsClosable()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool This property holds whether the tab bar should place close buttons on each tab in tabbed view mode..
Tabs are not closable by default.
- PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.tabsMovable()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool This property holds whether the user can move the tabs within the tabbar area in tabbed view mode..
Tabs are not movable by default.
See also
QTabBar.movable PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.setViewMode()
- PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.testOption(opton)¶
Parameters: opton – PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.AreaOption Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool Returns true if option is enabled; otherwise returns false.
See also
QMdiArea.AreaOption PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.setOption()
- PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.tileSubWindows()¶
Arranges all child windows in a tile pattern.
- PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.viewMode()¶
Return type: PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.ViewMode This property holds the way sub-windows are displayed in the PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea ..
By default, the SubWindowView is used to display sub-windows.
See also
QMdiArea.ViewMode PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.setTabShape() PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea.setTabPosition()




