QAbstractItemModel¶
Inherited by: Phonon.ObjectDescriptionModel, Phonon.EffectDescriptionModel, Phonon.AudioOutputDeviceModel, QAbstractTableModel, QSqlQueryModel, QSqlTableModel, QSqlRelationalTableModel, QHelpContentModel, QDirModel, QAbstractProxyModel, QSortFilterProxyModel, QStandardItemModel, QProxyModel, QFileSystemModel, QAbstractListModel, QStringListModel, QHelpIndexModel
Synopsis¶
Functions¶
- def beginInsertColumns (parent, first, last)
- def beginInsertRows (parent, first, last)
- def beginMoveColumns (sourceParent, sourceFirst, sourceLast, destinationParent, destinationColumn)
- def beginMoveRows (sourceParent, sourceFirst, sourceLast, destinationParent, destinationRow)
- def beginRemoveColumns (parent, first, last)
- def beginRemoveRows (parent, first, last)
- def beginResetModel ()
- def changePersistentIndex (from, to)
- def changePersistentIndexList (from, to)
- def createIndex (row, column, ptr)
- def createIndex (row, column[, id=0])
- def decodeData (row, column, parent, stream)
- def encodeData (indexes, stream)
- def endInsertColumns ()
- def endInsertRows ()
- def endMoveColumns ()
- def endMoveRows ()
- def endRemoveColumns ()
- def endRemoveRows ()
- def endResetModel ()
- def hasIndex (row, column[, parent=QModelIndex()])
- def insertColumn (column[, parent=QModelIndex()])
- def insertRow (row[, parent=QModelIndex()])
- def persistentIndexList ()
- def removeColumn (column[, parent=QModelIndex()])
- def removeRow (row[, parent=QModelIndex()])
- def reset ()
- def roleNames ()
- def setRoleNames (roleNames)
- def setSupportedDragActions (arg__1)
- def sibling (row, column, idx)
- def supportedDragActions ()
Virtual functions¶
- def buddy (index)
- def canFetchMore (parent)
- def columnCount ([parent=QModelIndex()])
- def data (index[, role=Qt.DisplayRole])
- def dropMimeData (data, action, row, column, parent)
- def fetchMore (parent)
- def flags (index)
- def hasChildren ([parent=QModelIndex()])
- def headerData (section, orientation[, role=Qt.DisplayRole])
- def index (row, column[, parent=QModelIndex()])
- def insertColumns (column, count[, parent=QModelIndex()])
- def insertRows (row, count[, parent=QModelIndex()])
- def itemData (index)
- def match (start, role, value[, hits=1[, flags=Qt.MatchFlags(Qt.MatchStartsWith|Qt.MatchWrap)]])
- def mimeData (indexes)
- def mimeTypes ()
- def parent (child)
- def removeColumns (column, count[, parent=QModelIndex()])
- def removeRows (row, count[, parent=QModelIndex()])
- def revert ()
- def rowCount ([parent=QModelIndex()])
- def setData (index, value[, role=Qt.EditRole])
- def setHeaderData (section, orientation, value[, role=Qt.EditRole])
- def setItemData (index, roles)
- def sort (column[, order=Qt.AscendingOrder])
- def span (index)
- def submit ()
- def supportedDropActions ()
Slots¶
- def resetInternalData ()
Signals¶
- def columnsAboutToBeInserted (parent, first, last)
- def columnsAboutToBeMoved (sourceParent, sourceStart, sourceEnd, destinationParent, destinationColumn)
- def columnsAboutToBeRemoved (parent, first, last)
- def columnsInserted (parent, first, last)
- def columnsMoved (parent, start, end, destination, column)
- def columnsRemoved (parent, first, last)
- def dataChanged (topLeft, bottomRight)
- def headerDataChanged (orientation, first, last)
- def layoutAboutToBeChanged ()
- def layoutChanged ()
- def modelAboutToBeReset ()
- def modelReset ()
- def rowsAboutToBeInserted (parent, first, last)
- def rowsAboutToBeMoved (sourceParent, sourceStart, sourceEnd, destinationParent, destinationRow)
- def rowsAboutToBeRemoved (parent, first, last)
- def rowsInserted (parent, first, last)
- def rowsMoved (parent, start, end, destination, row)
- def rowsRemoved (parent, first, last)
Detailed Description¶
The PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel class provides the abstract interface for item model classes.
The PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel class defines the standard interface that item models must use to be able to interoperate with other components in the model/view architecture. It is not supposed to be instantiated directly. Instead, you should subclass it to create new models.
The PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel class is one of the Model/View Classes and is part of Qt’s model/view framework .
If you need a model to use with a PySide.QtGui.QListView or a PySide.QtGui.QTableView , you should consider subclassing PySide.QtCore.QAbstractListModel or PySide.QtCore.QAbstractTableModel instead of this class.
The underlying data model is exposed to views and delegates as a hierarchy of tables. If you do not make use of the hierarchy, then the model is a simple table of rows and columns. Each item has a unique index specified by a PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex .
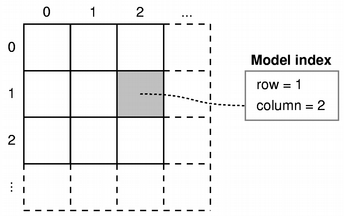
Every item of data that can be accessed via a model has an associated model index. You can obtain this model index using the PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.index() function. Each index may have a PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.sibling() index; child items have a PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.parent() index.
Each item has a number of data elements associated with it and they can be retrieved by specifying a role (see Qt.ItemDataRole ) to the model’s PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.data() function. Data for all available roles can be obtained at the same time using the PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.itemData() function.
Data for each role is set using a particular Qt.ItemDataRole . Data for individual roles are set individually with PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.setData() , or they can be set for all roles with PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.setItemData() .
Items can be queried with PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.flags() (see Qt.ItemFlag ) to see if they can be selected, dragged, or manipulated in other ways.
If an item has child objects, PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.hasChildren() returns true for the corresponding index.
The model has a PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.rowCount() and a PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.columnCount() for each level of the hierarchy. Rows and columns can be inserted and removed with PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.insertRows() , PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.insertColumns() , PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.removeRows() , and PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.removeColumns() .
The model emits signals to indicate changes. For example, PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.dataChanged() is emitted whenever items of data made available by the model are changed. Changes to the headers supplied by the model cause PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.headerDataChanged() to be emitted. If the structure of the underlying data changes, the model can emit PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.layoutChanged() to indicate to any attached views that they should redisplay any items shown, taking the new structure into account.
The items available through the model can be searched for particular data using the PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.match() function.
To sort the model, you can use PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.sort() .
Subclassing¶
Note
Some general guidelines for subclassing models are available in the Model Subclassing Reference .
When subclassing PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel , at the very least you must implement PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.index() , PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.parent() , PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.rowCount() , PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.columnCount() , and PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.data() . These functions are used in all read-only models, and form the basis of editable models.
You can also reimplement PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.hasChildren() to provide special behavior for models where the implementation of PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.rowCount() is expensive. This makes it possible for models to restrict the amount of data requested by views, and can be used as a way to implement lazy population of model data.
To enable editing in your model, you must also implement PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.setData() , and reimplement PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.flags() to ensure that ItemIsEditable is returned. You can also reimplement PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.headerData() and PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.setHeaderData() to control the way the headers for your model are presented.
The PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.dataChanged() and PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.headerDataChanged() signals must be emitted explicitly when reimplementing the PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.setData() and PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.setHeaderData() functions, respectively.
Custom models need to create model indexes for other components to use. To do this, call PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.createIndex() with suitable row and column numbers for the item, and an identifier for it, either as a pointer or as an integer value. The combination of these values must be unique for each item. Custom models typically use these unique identifiers in other reimplemented functions to retrieve item data and access information about the item’s parents and children. See the Simple Tree Model Example for more information about unique identifiers.
It is not necessary to support every role defined in Qt.ItemDataRole . Depending on the type of data contained within a model, it may only be useful to implement the PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.data() function to return valid information for some of the more common roles. Most models provide at least a textual representation of item data for the Qt.DisplayRole , and well-behaved models should also provide valid information for the Qt.ToolTipRole and Qt.WhatsThisRole . Supporting these roles enables models to be used with standard Qt views. However, for some models that handle highly-specialized data, it may be appropriate to provide data only for user-defined roles.
Models that provide interfaces to resizable data structures can provide implementations of PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.insertRows() , PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.removeRows() , PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.insertColumns() ,and PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.removeColumns() . When implementing these functions, it is important to notify any connected views about changes to the model’s dimensions both before and after they occur:
- An PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.insertRows() implementation must call PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.beginInsertRows() before inserting new rows into the data structure, and PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.endInsertRows() immediately afterwards.
- An PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.insertColumns() implementation must call PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.beginInsertColumns() before inserting new columns into the data structure, and PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.endInsertColumns() immediately afterwards.
- A PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.removeRows() implementation must call PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.beginRemoveRows() before the rows are removed from the data structure, and PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.endRemoveRows() immediately afterwards.
- A PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.removeColumns() implementation must call PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.beginRemoveColumns() before the columns are removed from the data structure, and PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.endRemoveColumns() immediately afterwards.
The private signals that these functions emit give attached components the chance to take action before any data becomes unavailable. The encapsulation of the insert and remove operations with these begin and end functions also enables the model to manage persistent model indexes correctly. If you want selections to be handled properly, you must ensure that you call these functions. If you insert or remove an item with children, you do not need to call these functions for the child items. In other words, the parent item will take care of its child items.
To create models that populate incrementally, you can reimplement PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.fetchMore() and PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.canFetchMore() . If the reimplementation of PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.fetchMore() adds rows to the model, PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.beginInsertRows() and PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.endInsertRows() must be called.
See also
Model Classes Model Subclassing Reference PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex PySide.QtGui.QAbstractItemView Using drag and drop with item views Simple DOM Model Example Simple Tree Model Example Editable Tree Model Example Fetch More Example
- class PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel([parent=None])¶
Parameters: parent – PySide.QtCore.QObject Constructs an abstract item model with the given parent .
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.beginInsertColumns(parent, first, last)¶
Parameters: - parent – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
- first – PySide.QtCore.int
- last – PySide.QtCore.int
Begins a column insertion operation.
When reimplementing PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.insertColumns() in a subclass, you must call this function before inserting data into the model’s underlying data store.
The parent index corresponds to the parent into which the new columns are inserted; first and last are the column numbers of the new columns will have after they have been inserted.
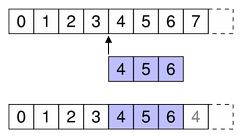
Specify the first and last column numbers for the span of columns you want to insert into an item in a model.
For example, as shown in the diagram, we insert three columns before column 4, so first is 4 and last is 6:
beginInsertColumns(parent, 4, 6)
This inserts the three new columns as columns 4, 5, and 6.
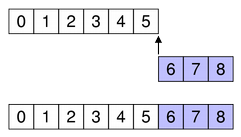
To append columns, insert them after the last column.
For example, as shown in the diagram, we append three columns to a collection of six existing columns (ending in column 5), so first is 6 and last is 8:
beginInsertColumns(parent, 6, 8)
This appends the two new columns as columns 6, 7, and 8.
Note
This function emits the PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.columnsAboutToBeInserted() signal which connected views (or proxies) must handle before the data is inserted. Otherwise, the views may end up in an invalid state.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.beginInsertRows(parent, first, last)¶
Parameters: - parent – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
- first – PySide.QtCore.int
- last – PySide.QtCore.int
Begins a row insertion operation.
When reimplementing PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.insertRows() in a subclass, you must call this function before inserting data into the model’s underlying data store.
The parent index corresponds to the parent into which the new rows are inserted; first and last are the row numbers that the new rows will have after they have been inserted.
Specify the first and last row numbers for the span of rows you want to insert into an item in a model.
For example, as shown in the diagram, we insert three rows before row 2, so first is 2 and last is 4:
beginInsertRows(parent, 2, 4)
This inserts the three new rows as rows 2, 3, and 4.
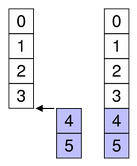
To append rows, insert them after the last row.
For example, as shown in the diagram, we append two rows to a collection of 4 existing rows (ending in row 3), so first is 4 and last is 5:
beginInsertRows(parent, 4, 5)
This appends the two new rows as rows 4 and 5.
Note
This function emits the PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.rowsAboutToBeInserted() signal which connected views (or proxies) must handle before the data is inserted. Otherwise, the views may end up in an invalid state.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.beginMoveColumns(sourceParent, sourceFirst, sourceLast, destinationParent, destinationColumn)¶
Parameters: - sourceParent – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
- sourceFirst – PySide.QtCore.int
- sourceLast – PySide.QtCore.int
- destinationParent – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
- destinationColumn – PySide.QtCore.int
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool
Begins a column move operation.
When reimplementing a subclass, this method simplifies moving entities in your model. This method is responsible for moving persistent indexes in the model, which you would otherwise be required to do yourself. Using beginMoveRows and endMoveRows is an alternative to emitting layoutAboutToBeChanged and layoutChanged directly along with changePersistentIndexes. layoutAboutToBeChanged is emitted by this method for compatibility reasons.
The sourceParent index corresponds to the parent from which the columns are moved; sourceFirst and sourceLast are the first and last column numbers of the columns to be moved. The destinationParent index corresponds to the parent into which those columns are moved. The destinationChild is the column to which the columns will be moved. That is, the index at column sourceFirst in sourceParent will become column destinationChild in destinationParent , followed by all other columns up to sourceLast .
However, when moving columns down in the same parent (sourceParent and destinationParent are equal), the columnss will be placed before the destinationChild index. That is, if you wish to move columns 0 and 1 so they will become columns 1 and 2, destinationChild should be 3. In this case, the new index for the source column i (which is between sourceFirst and sourceLast ) is equal to (destinationChild-sourceLast-1+i) .
Note that if sourceParent and destinationParent are the same, you must ensure that the destinationChild is not within the range of sourceFirst and sourceLast + 1. You must also ensure that you do not attempt to move a column to one of its own children or ancestors. This method returns false if either condition is true, in which case you should abort your move operation.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.beginMoveRows(sourceParent, sourceFirst, sourceLast, destinationParent, destinationRow)¶
Parameters: - sourceParent – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
- sourceFirst – PySide.QtCore.int
- sourceLast – PySide.QtCore.int
- destinationParent – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
- destinationRow – PySide.QtCore.int
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool
Begins a row move operation.
When reimplementing a subclass, this method simplifies moving entities in your model. This method is responsible for moving persistent indexes in the model, which you would otherwise be required to do yourself. Using beginMoveRows and endMoveRows is an alternative to emitting layoutAboutToBeChanged and layoutChanged directly along with changePersistentIndexes. layoutAboutToBeChanged is emitted by this method for compatibility reasons.
The sourceParent index corresponds to the parent from which the rows are moved; sourceFirst and sourceLast are the first and last row numbers of the rows to be moved. The destinationParent index corresponds to the parent into which those rows are moved. The destinationChild is the row to which the rows will be moved. That is, the index at row sourceFirst in sourceParent will become row destinationChild in destinationParent , followed by all other rows up to sourceLast .
However, when moving rows down in the same parent (sourceParent and destinationParent are equal), the rows will be placed before the destinationChild index. That is, if you wish to move rows 0 and 1 so they will become rows 1 and 2, destinationChild should be 3. In this case, the new index for the source row i (which is between sourceFirst and sourceLast ) is equal to (destinationChild-sourceLast-1+i) .
Note that if sourceParent and destinationParent are the same, you must ensure that the destinationChild is not within the range of sourceFirst and sourceLast + 1. You must also ensure that you do not attempt to move a row to one of its own children or ancestors. This method returns false if either condition is true, in which case you should abort your move operation.
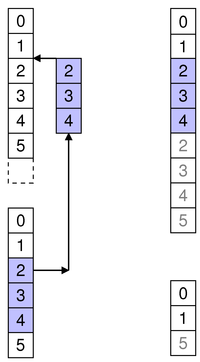
Specify the first and last row numbers for the span of rows in the source parent you want to move in the model. Also specify the row in the destination parent to move the span to.
For example, as shown in the diagram, we move three rows from row 2 to 4 in the source, so sourceFirst is 2 and sourceLast is 4. We move those items to above row 2 in the destination, so destinationChild is 2.
beginMoveRows(sourceParent, 2, 4, destinationParent, 2)
This moves the three rows rows 2, 3, and 4 in the source to become 2, 3 and 4 in the destination. Other affected siblings are displaced accordingly.
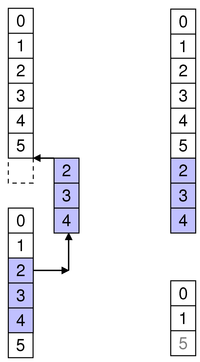
To append rows to another parent, move them to after the last row.
For example, as shown in the diagram, we move three rows to a collection of 6 existing rows (ending in row 5), so destinationChild is 6:
beginMoveRows(sourceParent, 2, 4, destinationParent, 6)
This moves the target rows to the end of the target parent as 6, 7 and 8.
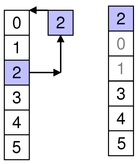
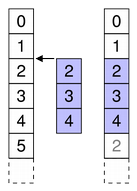
To move rows within the same parent, specify the row to move them to.
For example, as shown in the diagram, we move one item from row 2 to row 0, so sourceFirst and sourceLast are 2 and destinationChild is 0.
beginMoveRows(parent, 2, 2, parent, 0)
Note that other rows may be displaced accordingly. Note also that when moving items within the same parent you should not attempt invalid or no-op moves. In the above example, item 2 is at row 2 before the move, so it can not be moved to row 2 (where it is already) or row 3 (no-op as row 3 means above row 3, where it is already)
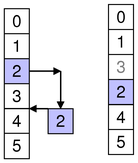
To move rows within the same parent, specify the row to move them to.
For example, as shown in the diagram, we move one item from row 2 to row 4, so sourceFirst and sourceLast are 2 and destinationChild is 4.
beginMoveRows(parent, 2, 2, parent, 4)
Note that other rows may be displaced accordingly.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.beginRemoveColumns(parent, first, last)¶
Parameters: - parent – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
- first – PySide.QtCore.int
- last – PySide.QtCore.int
Begins a column removal operation.
When reimplementing PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.removeColumns() in a subclass, you must call this function before removing data from the model’s underlying data store.
The parent index corresponds to the parent from which the new columns are removed; first and last are the column numbers of the first and last columns to be removed.
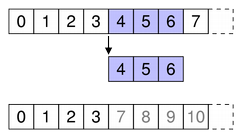
Specify the first and last column numbers for the span of columns you want to remove from an item in a model.
For example, as shown in the diagram, we remove the three columns from column 4 to column 6, so first is 4 and last is 6:
beginRemoveColumns(parent, 4, 6)
Note
This function emits the PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.columnsAboutToBeRemoved() signal which connected views (or proxies) must handle before the data is removed. Otherwise, the views may end up in an invalid state.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.beginRemoveRows(parent, first, last)¶
Parameters: - parent – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
- first – PySide.QtCore.int
- last – PySide.QtCore.int
Begins a row removal operation.
When reimplementing PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.removeRows() in a subclass, you must call this function before removing data from the model’s underlying data store.
The parent index corresponds to the parent from which the new rows are removed; first and last are the row numbers of the rows to be removed.
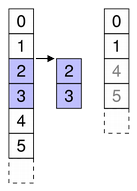
Specify the first and last row numbers for the span of rows you want to remove from an item in a model.
For example, as shown in the diagram, we remove the two rows from row 2 to row 3, so first is 2 and last is 3:
beginRemoveRows(parent, 2, 3)
Note
This function emits the PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.rowsAboutToBeRemoved() signal which connected views (or proxies) must handle before the data is removed. Otherwise, the views may end up in an invalid state.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.beginResetModel()¶
Begins a model reset operation.
A reset operation resets the model to its current state in any attached views.
Note
Any views attached to this model will be reset as well.
When a model is reset it means that any previous data reported from the model is now invalid and has to be queried for again. This also means that the current item and any selected items will become invalid.
When a model radically changes its data it can sometimes be easier to just call this function rather than emit PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.dataChanged() to inform other components when the underlying data source, or its structure, has changed.
You must call this function before resetting any internal data structures in your model or proxy model.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.buddy(index)¶
Parameters: index – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex Return type: PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex Returns a model index for the buddy of the item represented by index . When the user wants to edit an item, the view will call this function to check whether another item in the model should be edited instead. Then, the view will construct a delegate using the model index returned by the buddy item.
The default implementation of this function has each item as its own buddy.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.canFetchMore(parent)¶
Parameters: parent – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool Returns true if there is more data available for parent ; otherwise returns false.
The default implementation always returns false.
If PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.canFetchMore() returns true, PySide.QtGui.QAbstractItemView will call PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.fetchMore() . However, the PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.fetchMore() function is only called when the model is being populated incrementally.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.changePersistentIndex(from, to)¶
Parameters: - from – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
- to – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
Changes the PySide.QtCore.QPersistentModelIndex that is equal to the given from model index to the given to model index.
If no persistent model index equal to the given from model index was found, nothing is changed.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.changePersistentIndexList(from, to)¶
Parameters: - from – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndexList
- to – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndexList
Changes the QPersistentModelIndexes that is equal to the indexes in the given from model index list to the given to model index list.
If no persistent model indexes equal to the indexes in the given from model index list was found, nothing is changed.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.columnCount([parent=QModelIndex()])¶
Parameters: parent – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex Return type: PySide.QtCore.int Returns the number of columns for the children of the given parent .
In most subclasses, the number of columns is independent of the parent .
For example:
def columnCount(self, parent): return 3
Note
When implementing a table based model, PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.columnCount() should return 0 when the parent is valid.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.columnsAboutToBeInserted(parent, first, last)¶
Parameters: - parent – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
- first – PySide.QtCore.int
- last – PySide.QtCore.int
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.columnsAboutToBeMoved(sourceParent, sourceStart, sourceEnd, destinationParent, destinationColumn)¶
Parameters: - sourceParent – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
- sourceStart – PySide.QtCore.int
- sourceEnd – PySide.QtCore.int
- destinationParent – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
- destinationColumn – PySide.QtCore.int
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.columnsAboutToBeRemoved(parent, first, last)¶
Parameters: - parent – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
- first – PySide.QtCore.int
- last – PySide.QtCore.int
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.columnsInserted(parent, first, last)¶
Parameters: - parent – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
- first – PySide.QtCore.int
- last – PySide.QtCore.int
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.columnsMoved(parent, start, end, destination, column)¶
Parameters: - parent – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
- start – PySide.QtCore.int
- end – PySide.QtCore.int
- destination – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
- column – PySide.QtCore.int
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.columnsRemoved(parent, first, last)¶
Parameters: - parent – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
- first – PySide.QtCore.int
- last – PySide.QtCore.int
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.createIndex(row, column[, id=0])¶
Parameters: - row – PySide.QtCore.int
- column – PySide.QtCore.int
- id – PySide.QtCore.int
Return type: Use PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex QAbstractItemModel::createIndex(int row, int column, quint32 id) instead.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.createIndex(row, column, ptr)
Parameters: - row – PySide.QtCore.int
- column – PySide.QtCore.int
- ptr – PyObject
Return type: Creates a model index for the given row and column with the internal pointer ptr. When using a QSortFilterProxyModel, its indexes have their own internal pointer. It is not advisable to access this internal pointer outside of the model. Use the data() function instead. This function provides a consistent interface that model subclasses must use to create model indexes.
Warning
Because of some Qt/Python itegration rules, the ptr argument do not get the reference incremented during the QModelIndex life time. So it is necessary to keep the object used on ptr argument alive during the whole process. Do not destroy the object if you are not sure about that.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.data(index[, role=Qt.DisplayRole])¶
Parameters: - index – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
- role – PySide.QtCore.int
Return type: object
Returns the data stored under the given role for the item referred to by the index .
Note
If you do not have a value to return, return an invalidPySide.QtCore.QVariant instead of returning 0.
See also
Qt.ItemDataRole PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.setData() PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.headerData()
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.dataChanged(topLeft, bottomRight)¶
Parameters: - topLeft – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
- bottomRight – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.decodeData(row, column, parent, stream)¶
Parameters: - row – PySide.QtCore.int
- column – PySide.QtCore.int
- parent – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
- stream – PySide.QtCore.QDataStream
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.dropMimeData(data, action, row, column, parent)¶
Parameters: - data – PySide.QtCore.QMimeData
- action – PySide.QtCore.Qt.DropAction
- row – PySide.QtCore.int
- column – PySide.QtCore.int
- parent – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.encodeData(indexes, stream)¶
Parameters: - indexes – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndexList
- stream – PySide.QtCore.QDataStream
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.endInsertColumns()¶
Ends a column insertion operation.
When reimplementing PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.insertColumns() in a subclass, you must call this function after inserting data into the model’s underlying data store.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.endInsertRows()¶
Ends a row insertion operation.
When reimplementing PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.insertRows() in a subclass, you must call this function after inserting data into the model’s underlying data store.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.endMoveColumns()¶
Ends a column move operation.
When implementing a subclass, you must call this function after moving data within the model’s underlying data store.
layoutChanged is emitted by this method for compatibility reasons.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.endMoveRows()¶
Ends a row move operation.
When implementing a subclass, you must call this function after moving data within the model’s underlying data store.
layoutChanged is emitted by this method for compatibility reasons.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.endRemoveColumns()¶
Ends a column removal operation.
When reimplementing PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.removeColumns() in a subclass, you must call this function after removing data from the model’s underlying data store.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.endRemoveRows()¶
Ends a row removal operation.
When reimplementing PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.removeRows() in a subclass, you must call this function after removing data from the model’s underlying data store.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.endResetModel()¶
Completes a model reset operation.
You must call this function after resetting any internal data structure in your model or proxy model.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.fetchMore(parent)¶
Parameters: parent – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex Fetches any available data for the items with the parent specified by the parent index.
Reimplement this if you are populating your model incrementally.
The default implementation does nothing.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.flags(index)¶
Parameters: index – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex Return type: PySide.QtCore.Qt.ItemFlags Returns the item flags for the given index .
The base class implementation returns a combination of flags that enables the item (ItemIsEnabled ) and allows it to be selected (ItemIsSelectable ).
See also
Qt.ItemFlags
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.hasChildren([parent=QModelIndex()])¶
Parameters: parent – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool Returns true if parent has any children; otherwise returns false.
Use PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.rowCount() on the parent to find out the number of children.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.hasIndex(row, column[, parent=QModelIndex()])¶
Parameters: - row – PySide.QtCore.int
- column – PySide.QtCore.int
- parent – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool
Returns true if the model returns a valid PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex for row and column with parent , otherwise returns false.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.headerData(section, orientation[, role=Qt.DisplayRole])¶
Parameters: - section – PySide.QtCore.int
- orientation – PySide.QtCore.Qt.Orientation
- role – PySide.QtCore.int
Return type: object
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.headerDataChanged(orientation, first, last)¶
Parameters: - orientation – PySide.QtCore.Qt.Orientation
- first – PySide.QtCore.int
- last – PySide.QtCore.int
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.index(row, column[, parent=QModelIndex()])¶
Parameters: - row – PySide.QtCore.int
- column – PySide.QtCore.int
- parent – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
Return type: Returns the index of the item in the model specified by the given row , column and parent index.
When reimplementing this function in a subclass, call PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.createIndex() to generate model indexes that other components can use to refer to items in your model.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.insertColumn(column[, parent=QModelIndex()])¶
Parameters: - column – PySide.QtCore.int
- parent – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool
Inserts a single column before the given column in the child items of the parent specified.
Returns true if the column is inserted; otherwise returns false.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.insertColumns(column, count[, parent=QModelIndex()])¶
Parameters: - column – PySide.QtCore.int
- count – PySide.QtCore.int
- parent – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool
On models that support this, inserts count new columns into the model before the given column . The items in each new column will be children of the item represented by the parent model index.
If column is 0, the columns are prepended to any existing columns.
If column is PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.columnCount() , the columns are appended to any existing columns.
If parent has no children, a single row with count columns is inserted.
Returns true if the columns were successfully inserted; otherwise returns false.
The base class implementation does nothing and returns false.
If you implement your own model, you can reimplement this function if you want to support insertions. Alternatively, you can provide your own API for altering the data.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.insertRow(row[, parent=QModelIndex()])¶
Parameters: - row – PySide.QtCore.int
- parent – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool
Note
The base class implementation of this function does nothing and returns false.
Inserts a single row before the given row in the child items of the parent specified.
Returns true if the row is inserted; otherwise returns false.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.insertRows(row, count[, parent=QModelIndex()])¶
Parameters: - row – PySide.QtCore.int
- count – PySide.QtCore.int
- parent – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool
Note
The base class implementation of this function does nothing and returns false.
On models that support this, inserts count rows into the model before the given row . Items in the new row will be children of the item represented by the parent model index.
If row is 0, the rows are prepended to any existing rows in the parent.
If row is PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.rowCount() , the rows are appended to any existing rows in the parent.
If parent has no children, a single column with count rows is inserted.
Returns true if the rows were successfully inserted; otherwise returns false.
If you implement your own model, you can reimplement this function if you want to support insertions. Alternatively, you can provide your own API for altering the data. In either case, you will need to call PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.beginInsertRows() and PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.endInsertRows() to notify other components that the model has changed.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.itemData(index)¶
Parameters: index – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex Return type: Returns a map with values for all predefined roles in the model for the item at the given index .
Reimplement this function if you want to extend the default behavior of this function to include custom roles in the map.
See also
PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.setItemData() Qt.ItemDataRole PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.data()
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.layoutAboutToBeChanged()¶
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.layoutChanged()¶
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.match(start, role, value[, hits=1[, flags=Qt.MatchFlags(Qt.MatchStartsWith|Qt.MatchWrap)]])¶
Parameters: - start – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
- role – PySide.QtCore.int
- value – object
- hits – PySide.QtCore.int
- flags – PySide.QtCore.Qt.MatchFlags
Return type: PySide.QtCore.QModelIndexList
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.mimeData(indexes)¶
Parameters: indexes – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndexList Return type: PySide.QtCore.QMimeData Returns an object that contains serialized items of data corresponding to the list of indexes specified. The formats used to describe the encoded data is obtained from the PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.mimeTypes() function.
If the list of indexes is empty, or there are no supported MIME types, 0 is returned rather than a serialized empty list.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.mimeTypes()¶
Return type: list of strings Returns a list of MIME types that can be used to describe a list of model indexes.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.modelAboutToBeReset()¶
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.modelReset()¶
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.parent(child)¶
Parameters: child – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex Return type: PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex Returns the parent of the model item with the given index . If the item has no parent, an invalid PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex is returned.
A common convention used in models that expose tree data structures is that only items in the first column have children. For that case, when reimplementing this function in a subclass the column of the returned PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex would be 0.
When reimplementing this function in a subclass, be careful to avoid calling PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex member functions, such as QModelIndex.parent() , since indexes belonging to your model will simply call your implementation, leading to infinite recursion.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.persistentIndexList()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.QModelIndexList Returns the list of indexes stored as persistent indexes in the model.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.removeColumn(column[, parent=QModelIndex()])¶
Parameters: - column – PySide.QtCore.int
- parent – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool
Removes the given column from the child items of the parent specified.
Returns true if the column is removed; otherwise returns false.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.removeColumns(column, count[, parent=QModelIndex()])¶
Parameters: - column – PySide.QtCore.int
- count – PySide.QtCore.int
- parent – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool
On models that support this, removes count columns starting with the given column under parent parent from the model.
Returns true if the columns were successfully removed; otherwise returns false.
The base class implementation does nothing and returns false.
If you implement your own model, you can reimplement this function if you want to support removing. Alternatively, you can provide your own API for altering the data.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.removeRow(row[, parent=QModelIndex()])¶
Parameters: - row – PySide.QtCore.int
- parent – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool
Removes the given row from the child items of the parent specified.
Returns true if the row is removed; otherwise returns false.
This is a convenience function that calls PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.removeRows() . The PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel implementation of PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.removeRows() does nothing.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.removeRows(row, count[, parent=QModelIndex()])¶
Parameters: - row – PySide.QtCore.int
- count – PySide.QtCore.int
- parent – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool
On models that support this, removes count rows starting with the given row under parent parent from the model.
Returns true if the rows were successfully removed; otherwise returns false.
The base class implementation does nothing and returns false.
If you implement your own model, you can reimplement this function if you want to support removing. Alternatively, you can provide your own API for altering the data.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.reset()¶
Resets the model to its original state in any attached views.
Note
Use PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.beginResetModel() and PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.endResetModel() instead whenever possible. Use this method only if there is no way to call PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.beginResetModel() before invalidating the model. Otherwise it could lead to unexpected behaviour, especially when used with proxy models.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.resetInternalData()¶
This slot is called just after the internal data of a model is cleared while it is being reset.
This slot is provided the convenience of subclasses of concrete proxy models, such as subclasses of PySide.QtGui.QSortFilterProxyModel which maintain extra data.
<Code snippet "doc/src/snippets/code/src_corelib_kernel_qabstractitemmodel.cpp:10" not found>
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.revert()¶
Lets the model know that it should discard cached information. This function is typically used for row editing.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.roleNames()¶
Return type: Returns the model’s role names.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.rowCount([parent=QModelIndex()])¶
Parameters: parent – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex Return type: PySide.QtCore.int Returns the number of rows under the given parent . When the parent is valid it means that rowCount is returning the number of children of parent.
Note
When implementing a table based model, PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.rowCount() should return 0 when the parent is valid.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.rowsAboutToBeInserted(parent, first, last)¶
Parameters: - parent – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
- first – PySide.QtCore.int
- last – PySide.QtCore.int
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.rowsAboutToBeMoved(sourceParent, sourceStart, sourceEnd, destinationParent, destinationRow)¶
Parameters: - sourceParent – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
- sourceStart – PySide.QtCore.int
- sourceEnd – PySide.QtCore.int
- destinationParent – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
- destinationRow – PySide.QtCore.int
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.rowsAboutToBeRemoved(parent, first, last)¶
Parameters: - parent – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
- first – PySide.QtCore.int
- last – PySide.QtCore.int
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.rowsInserted(parent, first, last)¶
Parameters: - parent – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
- first – PySide.QtCore.int
- last – PySide.QtCore.int
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.rowsMoved(parent, start, end, destination, row)¶
Parameters: - parent – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
- start – PySide.QtCore.int
- end – PySide.QtCore.int
- destination – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
- row – PySide.QtCore.int
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.rowsRemoved(parent, first, last)¶
Parameters: - parent – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
- first – PySide.QtCore.int
- last – PySide.QtCore.int
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.setData(index, value[, role=Qt.EditRole])¶
Parameters: - index – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
- value – object
- role – PySide.QtCore.int
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool
Sets the role data for the item at index to value .
Returns true if successful; otherwise returns false.
The PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.dataChanged() signal should be emitted if the data was successfully set.
The base class implementation returns false. This function and PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.data() must be reimplemented for editable models.
See also
Qt.ItemDataRole PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.data() PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.itemData()
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.setHeaderData(section, orientation, value[, role=Qt.EditRole])¶
Parameters: - section – PySide.QtCore.int
- orientation – PySide.QtCore.Qt.Orientation
- value – object
- role – PySide.QtCore.int
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.setItemData(index, roles)¶
Parameters: - index – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
- roles –
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.setRoleNames(roleNames)¶
Parameters: roleNames –
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.setSupportedDragActions(arg__1)¶
Parameters: arg__1 – PySide.QtCore.Qt.DropActions
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.sibling(row, column, idx)¶
Parameters: - row – PySide.QtCore.int
- column – PySide.QtCore.int
- idx – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex
Return type: Returns the sibling at row and column for the item at index , or an invalid PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex if there is no sibling at that location.
PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.sibling() is just a convenience function that finds the item’s parent, and uses it to retrieve the index of the child item in the specified row and column .
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.sort(column[, order=Qt.AscendingOrder])¶
Parameters: - column – PySide.QtCore.int
- order – PySide.QtCore.Qt.SortOrder
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.span(index)¶
Parameters: index – PySide.QtCore.QModelIndex Return type: PySide.QtCore.QSize Returns the row and column span of the item represented by index .
Note
Currently, span is not used.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.submit()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool Lets the model know that it should submit cached information to permanent storage. This function is typically used for row editing.
Returns true if there is no error; otherwise returns false.
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.supportedDragActions()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.Qt.DropActions Returns the actions supported by the data in this model.
The default implementation returns PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.supportedDropActions() unless specific values have been set with PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.setSupportedDragActions() .
PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.supportedDragActions() is used by QAbstractItemView.startDrag() as the default values when a drag occurs.
See also
PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.setSupportedDragActions() Qt.DropActions Using drag and drop with item views
- PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.supportedDropActions()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.Qt.DropActions Returns the drop actions supported by this model.
The default implementation returns Qt.CopyAction . Reimplement this function if you wish to support additional actions. You must also reimplement the PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.dropMimeData() function to handle the additional operations.
See also
PySide.QtCore.QAbstractItemModel.dropMimeData() Qt.DropActions Using drag and drop with item views




